
https://ec.europa.eu/eip/agriculture/en/find-connect/projects/bovine-beef-innovation-network-europe
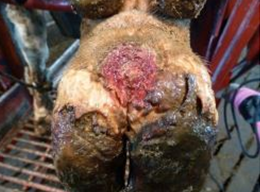
Digital dermatitis (DD), often referred to as hairy heel warts, is an infectious foot disease in dairy and beef cattle herds. The size and scope of digital dermatitis within the beef industry is undetermined but is a growing concern. Once introduced to the herd, the disease can spread rapidly reaching prevalence of 70%.The most common bacteria found is Treponema spp. The disease begins when the integrity of the skin is compromised and, if untreated, the lesions caused by it can lead to severe and debilitating lameness. The impact caused by lameness on the animal's performance is vast and has significant costs by reducing the average daily gain in fattening/finishing cattle. Digital dermatitis is introduced on the farm in several ways, such as, the introduction of infected animals, lack of hygiene, inadequate trimming/pediluvios. Continuous humidity and physical or chemical trauma can also lead to the appearance of the lesions. One of the difficulties in combating digital Dermatitis is early and correct detection, before there is a reservoir of disease from encysted bacteria deep in the skin. The correct diagnose is not only important for the treatment of the lame animals, but also helps develop a prevention program for the other animals.
Step-Up® Management Program to identify, diagnose and treat lameness
As a part of the Step-Up® Management Program for Beef Cattle, Zinpro has developed a diagnostic guide to help identify the underlying causes of lameness in cattle in order to recommend appropriate management strategies. The decision tree walks beef producers through the steps of identifying hoof lesions correctly. Download the beef cattle lameness decision tree here. The Step-Up® App, a free resource to help manage beef cattle lameness, offers access to training resources and includes an easy-to-use diagnostic guide to help users determine the cause of lameness in their herd https://www.zinpro.com/lameness/beef/step-up-app
Next to these diagnostic tools proper management is part of the strategy by Zinpro. They recommend to prevent infected animals being introduced into the herd, promote a clean, dry environment and propose to use footbaths as needed. In addition, trace elements are promoted to improve skin integrity and immune function in animals. Zinc is the main contributor because of its role in epithelial skin integrity. It is important both to the development of new skin cells and in wound healing.
Literature:
Gomez, A. (2018): Dermatite digital. A visao do especialista em patologia podal. https://issuu.com/ruminantes/docs/ruminantes31 (see page 64)
Further information about digital dermatitis from the dairy sector
For digital dermatitis, a distinction is made between different stages of the disease as well as between different types of cows. These are described under the following link https://www.zinpro.com/Portals/0/Docs/DynamicsofDD_DopferPaper.pdf
In order to improve the detection of digital dermatitis (in the dairy sector), the so-called "DD Check APP" was developed at the University of Madison / Wisconsin with Zinpro. The following link leads to information about digital dermatitis (cycle of disease progression, Download DD Check app).https://www.zinpro.com/lameness/digital-dermatitis#m41
In digital dermatitis control, it is essential to have a strategy that includes management, hygiene and nutrition. Please see Good practice hoof sanitization for more information about infectious hoof disease.
This Research Innovation has an Impact on:
- Socio-economic resilience: Improvement of health and welfare always reflects in higher incomes and production.
- Animal health and welfare: By choosing to control and prevent digital dermatitis, the health and well-being of the animals will improve, since it will not give place for the pain and discomfort caused by it.
In terms of infectious claw disorders there are some more articles on the BovINE Knowledge Hub:
Preventing digital dermatitis
Prevention of Digital Dermatitis in housed beef cattle
On farm hoof sanitization